Social entrepreneurship has become an effective method to address critical social economic and environmental problems that face humanity today. The core distinction of social entrepreneurship versus traditional entrepreneurship is that social enterprises merge business abilities with societal effect to develop sustainable solutions which benefit communities. This paper examines social entrepreneurship in extensive detail starting from its history and importance all the way to its obstacles along with new approaches and community-economic effects and future potential and its groundbreaking impact worldwide and across India.

👉Understanding Social Entrepreneurship :-
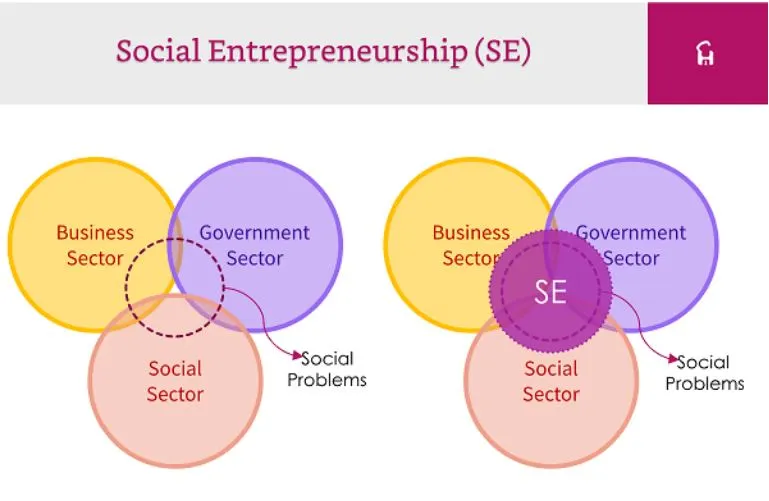
Social Entrepreneurship describes how individuals or groups or organizations develop funding and execute solutions to social cultural and environmental challenges through business-oriented principles. The entrepreneurial model incorporates nonprofit organization dedication to purpose alongside business enterprise methods for innovation along with sustainability and scalability. Social entrepreneurs locate under addressed social challenges including poverty, education deficits, health service limitations and environmental concerns and employment barriers and establish profitable solutions to these issues.
Since the early 2000s the movement has grown into an established field which now lures policymakers along with investors and academics. The approach of social entrepreneurship expands business functions to include philanthropic and activist principles which results in introducing enterprises that serve economic and social goals.
👉Drivers Behind the Rise of Social Entrepreneurship :-
Numerous elements have led to the worldwide expansion of social entrepreneurship.
⏩Growing Social Awareness :- Social awareness is growing rapidly because people along with organizations now understand how global inequalities accompany environmental degradation and social injustices so these groups seek solutions that transcend traditional charity work and governmental programs.
⏩Limitations of Traditional Approaches :- Traditional business operations avoid minority populations while government programs face difficulties in both broad implementation and developing original solutions. The market-driven approach coupled with social objectives which social entrepreneurship creates allows it to fill the deficiencies that exist in both private enterprise and government services.
⏩Entrepreneurial Spirit with Purpose :- Social entrepreneurs combine entrepreneurial spirit with a mission to produce meaningful social change by using their business capabilities to realize their purpose.
⏩Supportive Ecosystems :- Social enterprise development receives support from the establishment of incubators accelerators impact investment funds and academic programs focused on social entrepreneurship.
⏩Technological Advancements :- Technology helps social entrepreneurs reach large audiences through improved operations which allows them to measure their social impact effectively.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Social_entrepreneurship
👉Innovative Business Models and Strategies :-
Social entrepreneurs establish multiple business approaches to merge financial profitability with social mission delivery. Some common models include:
⏩Hybrid Models :- Hybrid profit-sustaining models join revenue generation businesses with social services so enterprises have financial stability to deliver social benefits.
⏩Collaborative Partnerships :- Social enterprises establish partnerships with public institutions as well as non-profit organizations and private sector entities in order to achieve widespread social impact through effective resource sharing.
⏩Technology Driven Solutions :- Social entrepreneurs use technology platforms along with data analytics and mobile systems to build outreach programs which enhance delivery services.
⏩Community Based Approaches :- Through community-based approaches social enterprises activate local communities by making them partakers in decision-making and developing solutions that address neighborhood issues.
The services IBM Corporate Service Corps provides free consulting to communities which develops IBM employee leadership skills thus demonstrating a triple-win approach.
👉Socio-Economic Impact of Social Entrepreneurship :-
Social entrepreneurship drives substantial social and economic developments throughout developing countries particularly India:
⏩Job Creation & Income Generation :- Through their enterprise activities social organizations create jobs which focus primarily on marginalized communities thereby reducing poverty and improving life standards.
⏩Inclusive Economic Growth :- Social entrepreneurship creates inclusive economic growth when it targets underserved areas to establish more equitably developed society.
⏩Improved Access to Services :- Social enterprises create better service access for communities by providing essential education together with healthcare facilities as well as clean energy and other vital services which supports general social welfare.
⏩Sustainable Development :- Social entrepreneurship promotes sustainable development through its emphasis on environmentally friendly procedures while maintaining economic growth pay-offs from nature protection.
Social entrepreneurship throughout India has proven beneficial for economic development through job creation combined with income rise and higher quality of life across both rural and urban zones.

👉Challenges Facing Social Entrepreneurship :-
Social entrepreneurship continues to encounter several difficulties even though it shows great promise.
⏩Identifying the Right Problems :- Social entrepreneurs frequently address problems which are either speculative or studied insufficiently which makes solution development and prediction very challenging.
⏩Funding & Finding Sustainability :- Social entrepreneurship frequently face hurdles in obtaining enough funding support from investors because investors demonstrate higher reluctance toward social ventures. Social entrepreneurship faces challenges when attempting to recruit and maintain skilled personnel because of salary differences with commercial enterprises.
⏩Balancing Social & Business Goals :- Social ventures must achieve profitability alongside social goals through innovative business design that needs frequent adjustments because these processes are expensive and complex to maintain.
⏩Scaling Impact :- A wide range of social initiatives struggle to expand to broader audiences since they keep operating at local scales. Social entrepreneurs encounter obstacles to expansion and sustainability due to weak partnerships between themselves and government agencies.
⏩Public Perception & Standardization :- Impact measurement standards that are not standardized alongside public doubts about social entrepreneurship success prevent supporters from growing their investment in these ventures.
👉The Role of Policy and Ecosystem Support :-
Social entrepreneurship needs functioning ecosystems together with favorable policy structures for proper growth and sustainability.
⏩Policy Frameworks :- Government agencies should create specific policies together with financial aids and support structures to help social enterprises thrive.
⏩Cross-Sector Collaboration :- The establishment of government-NGO-private corporation partnerships helps organizations distribute resources while improving accountability and increases their impact potential.
⏩Capacity Building :- Success requires social entrepreneurs to receive training which provides them with business competencies and market awareness alongside leadership development.
⏩Impact Measurement :- Social organizations can obtain investment through enhanced transparency by developing strong systems that measure social performance in addition to financial metrics.
👉Future Prospects and Paradigm Shift :-
Social Entrepreneurship introduces a new approach to both business thinking and development practice. The business approach of social entrepreneurship goes beyond profit orientation to connect social purposes with economic operations thereby creating both inclusive development and sustainability. Enhanced effectiveness of the field will result from growing involvement of policymakers alongside investors and academic institutions.
Social entrepreneurship demonstrates great potential to reform economic systems and social structures mostly because it fills the voids within traditional development methods while building a fairer and lasting environment in emerging markets like India.
Social entrepreneurship represents a fundamental transformation which uses entrepreneurial creativity to persistently tackle complex social challenges using sustainable methods. In spite of existing obstacles the innovative structures combined with economic advantages and expanding community backing position it as a fundamental tool for worldwide development that includes all social groups and relies on sustainability.

👉Key Challenges Faced by Social Entrepreneurs :-
Social entrepreneurship solve complicated social along with environmental and economic problems by developing mission-based business models with innovative practices. Social entrepreneurs face various obstacles which block their path toward developing enduring social impact. Available expert studies show that social entrepreneurs encounter these main difficulties during their present operations.
1. Financial Sustainability and Funding Constraints :-
Social entrepreneurs encounter financial sustainability along with funding as their most critical obstacle. Social enterprises need to maintain both profit generation and social goal achievement while operating their organizations. Social entrepreneurs face increased challenges when seeking investor backing because most impact investors require long-term returns extending to 5-7 years although this time span discourages funding opportunities.
Social entrepreneurship find it difficult to obtain funding through various channels because they have trouble developing financial models and communicating their organizational value effectively enough to investors. The scarcity of funds prevents social entrepreneurs from expanding their operations while building necessary infrastructure and providing sufficient compensation to staff members which puts their business at risk.
2. Scaling Impact :-
Proliferating social impact from first community reach or first markets represents a repeated barrier. Social entrepreneurship experience multiple difficulties including limited resources together with insufficient infrastructure and regulatory restrictions which prevent them from properly expanding their operations. The quality of service delivery becomes more challenging when a social organization grows rapidly because hasty scale-up often results in diminished social impact if proper management is lacking.
Reaching success would prove difficult when trying to duplicate effective models between different situations which contain distinct social and cultural elements. The process demands flexible approaches and joint efforts between operators and local partners as well as governmental institutions for maintaining lasting growth.
3. Measuring and Demonstrating Social Impact :-
Social enterprises must track intangible social results instead of financial data because traditional businesses measure financial metrics. This tracking method becomes complex. Building dependable monitoring systems for impact assessment requires extensive time and funding resources. The process of showing distinct social results remains essential to secure financial backing and secure user trust and substantiate operational effectiveness.
Social entrepreneurs typically do not have access to standardized impact measurement tools or expertise for convincing impact communication thus leading to decreased donor and investor and beneficiary trust.
4. Navigating Regulatory and Legal Complexities :-
Social entrepreneurs must practice their work in sectors such as education and healthcare and environmental conservation under strict regulatory environments. Implementation of social entrepreneurship faces operational difficulties due to complex legal structures together with mandatory licensing needs and regulatory taxes. The process of compliance requires detailed strategic planning together with regulatory entities but uses substantial resources and delays operational speed and service delivery.
Many jurisdictions fail to establish clear legal definitions for social enterprises thus making it difficult for these organizations to gain benefits which include tax exemptions and government support.
5. Balancing Stakeholders Interest & Ethical Dilemma :-
Social entrepreneurs need to handle multiple stakeholder interests which may compete against one another involving beneficiaries alongside investors and employees and communities. Social entrepreneurs face ethical challenges because decisions positive for one group often have negative effects on others. The effective management of social enterprises demands skilled handling between transparent leadership which upholds social core principles and successful financial performance and operational needs of stakeholders.
The application of proper balance between stakeholders’ needs forms a crucial requirement for social enterprises to maintain their trustworthiness and official authorization despite the ever-evolving challenges.
6. Overcoming Resistance to Change :-
Social entrepreneurship exists by nature as a disruptive force which opposes traditional systems because it disturbs established norms. Traditional institutions alongside existing competitors and beneficiary users of current services commonly show resistance to new approaches. Establishing new models in society needs continuous support together with diplomatic relationships and strategic alliances for their successful integration.
Social enterprises experience resistance because people doubt their intentions and effectiveness in which case they need to establish trustworthiness coupled with concrete results.
7. Limited Awareness and Market Penetration :-
Social enterprise businesses face significant barriers when trying to expand their customer base outside targeted population segments. The limited awareness of customers regarding social enterprise products and services restricts market penetration along with revenue growth. Digital and social media strategies serve as main marketing tools but they fail to target audiences who are unaware of the social enterprise platform and its purpose.
Social enterprises must invest their resources into brand development and marketing and sales capabilities and communication strategies to expand beyond niche audiences despite the challenge being resource-intensive.
8. Skills Gaps and Need for Support :-
The strong subject matter expertise of social entrepreneurs often exists alongside a deficiency of needed operational and business and marketing skills for venture growth and sustainability. The lack of connection to expert mentors and peer networks along with limited access to verification from specialists causes social entrepreneurs to experience uncertainty when making critical choices while also feeling isolated.
Social entrepreneurs require training and consulting and community support to receive essential skills for their leadership and management roles.
9. Risk of Burnout and Emotional Exhaustion :
Long-term commitment to running social enterprises results in burnout for social entrepreneurs because they work under limited resources and high pressure. Mission-oriented work creates both emotional and physical strain when social entrepreneurs maintain operational commitments. The duration of motivation and resilience demands proper individual care and effective teamwork with adequate support networks.
The path of social entrepreneurs is obstructed by various kinds of challenges which extend from financial aspects to operational difficulties and regulatory obstacles and impact the entrepreneur personally. Social entrepreneurs need to demonstrate resilience along with innovative ideas and powerful networks and supportive ecosystems that include funding bodies as well as governments and communities to overcome these obstacles. Social entrepreneurs push transformative social change through their adaptive approaches to obstacles that stand in their way despite these obstacles existing.
👉Innovative Strategies used by Social Enterprises :-
⏩Leveraging Technology for Efficiency & Reach :-
Technological resources enable social enterprises to become more efficient and reach all their potential beneficiaries better. Social enterprises use technology as an enabling tool to execute automated workflows and improve internal communication and develop data-based decision systems. Digital platforms enable social enterprises to expand their operations which leads to better service delivery to beneficiaries.
⇒Example :- The online system of Kiva operates as a micro-lending platform which provides automated loan processing while lowering operational costs to help speed up impact delivery.
The application of data analytics and artificial intelligence tools has become common practice for organizations that monitor social programs through performance assessment while distributing resources more effectively and predicting program results as exemplified by Crisis Text Line and similar organizations using data analytics to achieve better social outcomes.
⏩Implementing Lean Principles & Operational Efficiency :-
Through lean methodologies social enterprises gain effective operation alignment and improved workflow and eliminate unnecessary expenses which frees up resources for better allocation.
⇒Example :- The lean manufacturing methods implemented by Greyston Bakery allow the organization to cut down on waste while achieving both social and financial success through improved production efficiency.
⏩Outsourcing Non-Core Activities :-
Social enterprises who work with specialized partners for logistics distribution and administrative tasks will enhance their operational efficiency because it allows them to dedicate resources toward their core mission.
⇒Example :- The outsourcing of logistics functions to local partners by Solar Sister allows the enterprise to focus on developing and empowering rural African female entrepreneurs who sell solar products.
⏩Fostering a Culture of Innovation and Adaptability:-
The practice of allowing employees and stakeholders to submit new ideas enables social enterprises to maintain relevance and adaptiveness toward evolving needs.
⇒Example :- At Warby Parker staff members receive creative authority to create new programs including the home try-on service that enhances buying convenience and improves customer satisfaction.
⏩Utilizing Innovative Business Models :-
Social enterprises implement distinctive business approaches which unite business profits with purposeful activities to achieve enduring social impact.
One-for-One Model :- This business model donates a product to needy individuals whenever an organization sells one of its products. TOMS Shoes led this business model by donating more than 100 million pairs of shoes across the world.
Circular Economy :- In this, one must create products that can be reused or recycled or implement closed-loop systems together with sharing economy principles to minimize waste while generating financial value.
Social Franchising :- These organizations can expand successful social enterprise models by using franchise partnerships to achieve growth with no compromise on their mission.
Hybrid Models :- It combine nonprofit elements with for-profit structures to unite benefits from both sectors into balanced approaches between financial longevity and social performance enhancement.
⏩Business Strategic Partnerships & Ecosystems :-
The formation of public-private alliances with government bodies and NGOs along with corporations and community organizations enables organizations to obtain vital resources and specialized knowledge and extensive networks which leads to larger-scale impact.
⇒Example :- Ikea partners with its social entrepreneurship initiative and Northwest Center joins with Amazon to expand their operations while increasing their outreach abilities.
The collaborative efforts between different sectors enable organizations to exchange expertise and create customized solutions and conduct advocacy for improved policies which address community requirements.
⏩Data-Driven Impact Measurement and Reporting :-
Strong impact measurement systems within social enterprises help organizations measure social impacts while increasing transparency levels which enables them to secure more investment.
Through balanced scorecards and lean data principles social enterprises track their progress while making adjustments to their strategies using current feedback.
Social enterprises can successfully negotiate with investors through impact measurement because it allows detailed communication between social achievements and financial data.
⏩Strategic Branding and Market Positioning
Social enterprises establish customer loyalty through branding development and marketing methodology which helps them stand apart from market competition.
Customers who look for products with social significance strongly respond to stories that communicate social impact.
⏩Co-Designing Solutions with Communities :-
The implementation of programs through beneficiary-engagement in design stages produces results that remain relevant over time and receive widespread acceptance and continue functional throughout long periods.
The method of active community participation produces better program results and builds community self-assurance.
⏩Embracing Digital Transformation & Social Media :-
Social media marketing enables organizations to expand their audience base while showing greater clarity about operations while attracting worldwide backing.
Blockchain technology demonstrates strong capability to track supply chains and ethical sourcing by utilizing its supply chain transparency features.
👉Conclusion :-
Social enterprises achieve success through the integration of modern technology with unique business models together with strategic alliances and data-oriented management processes and the establishment of innovative communities and community engagement culture. Such business strategies help organizations sustain impact growth without sacrificing their social and economic goals.
💬Disclaimer :-
This Blog provides general information as an educational source only. The author uses their life experiences together with personal viewpoints to create all content. The author accepts no responsibility for damages or losses when users apply this information. The website information depends on your individual acceptance of personal risk when you use it. The information does not serve as professional guidance, so readers need to seek proper professional advice before implementing decisions from the provided content.